Introduction
Introduction
Generative AI
Generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) is a cutting-edge technology with the potential to transform many industries. Unlike typical AI models that spot patterns in data, generative AI can produce entirely new data that looks just like human-made content. They can take a small input and create realistic new outputs based on what they’ve learned. This means AI isn’t just analyzing our world anymore; it’s also creating in it.
Some popular generators for text are GPT-3/4 (ChatGPT), Anthropic Claude, and Amazon Titan, and for image DALL-E 2/3. There are generators for video and music as well.
Generative AI is powered by machine learning models that have been trained on a massive amount of data over weeks and months. Most of these foundation models (FMs) are based on neural network architecture.
Text Generative AI

Text generative AI models try to predict the next word given the current sequence of words. The models do this by generating a probability score for each word in their vocabulary and picking the word with the highest probability score for the next generation.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique where a model combines the retrieval of relevant information with generative capabilities to answer questions or provide information.
Imagine you’re curious about Cyprus’s history. With RAG, it’s like having a knowledgeable historian by your side. First, RAG searches through historical records and articles about Cyprus (that’s the retrieval part). Then, it not only provides you with key historical facts but also helps you craft a detailed narrative or explanation using the retrieved information (that’s the generation part). For instance, if you inquire about ancient landmarks in Cyprus, RAG might retrieve details about sites like the ancient city of Salamis or the Tombs of the Kings and then use that information to describe their significance or historical context. The combination of finding and crafting responses makes RAG-enabled chatbots exceptionally useful and engaging.
How are generative AI models used today?
Generative AI models are already used in a lot of different ways. In healthcare, they help doctors analyze images and find diseases early (aidoc). For art and design, they help create cool pictures, music, and stories. In talking with chatbots or translating languages, they make computers understand and talk more like us. Overall, they’re everywhere, and we are only at the beginning!
Workshop Architecture
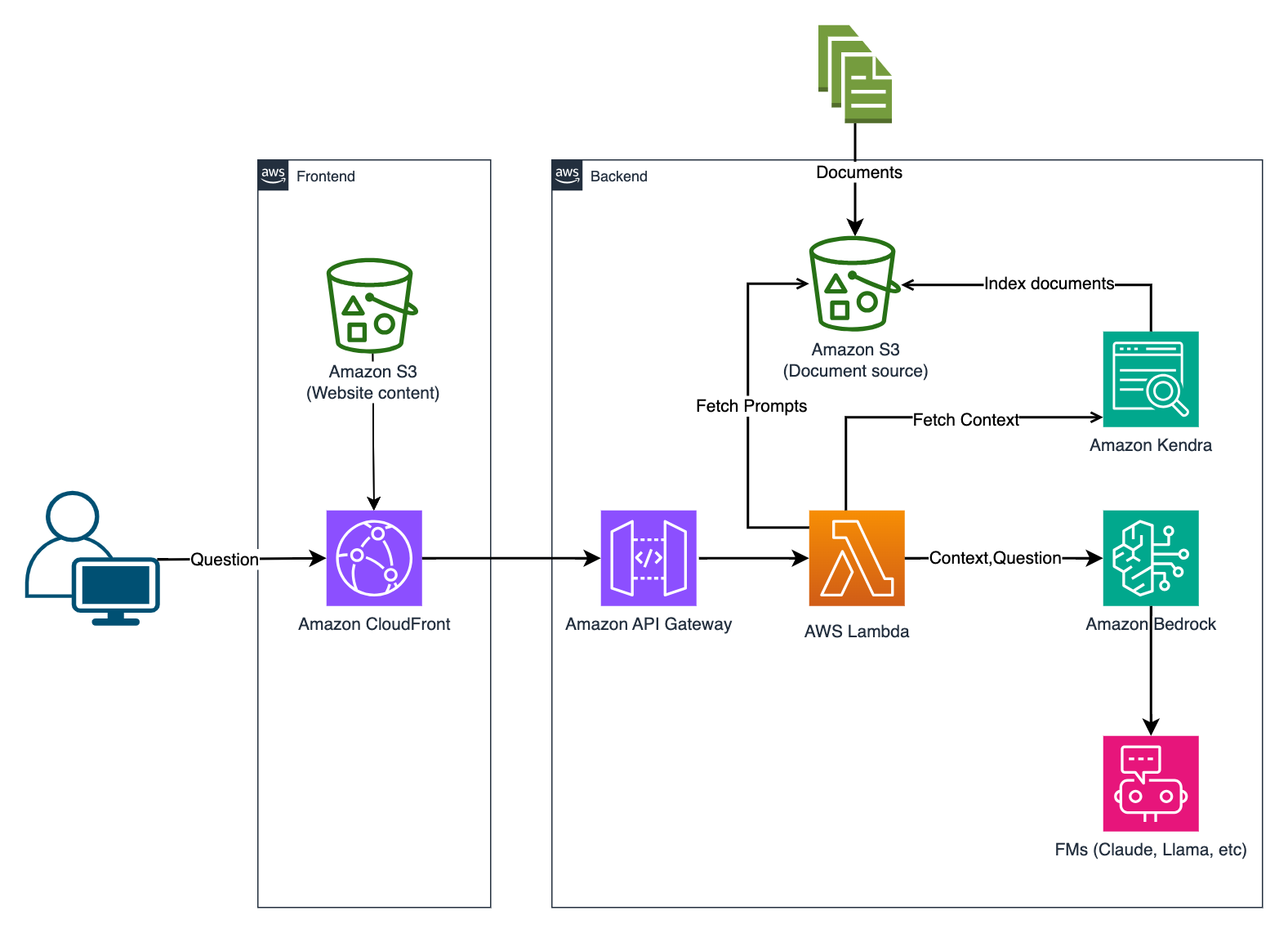
A user interacts with the chatbot through a website. The user’s query passes through CloudFront and API Gateway to Lambda, which retrieves content from Kendra, and uses Bedrock’s foundation models to generate a response. The response is then returned to the user. This architecture leverages various AWS services for a scalable, efficient solution.
- Documents: The documents serve as the primary source of content for the chatbot.
- Amazon S3: Stores the documents and acts as a centralized repository allowing for efficient storage and retrieval.
- Amazon Kendra: Vector database for indexing the documents from Amazon S3. Provides easy search and retrieval of relevant content.
- Amazon Bedrock: Provides access to foundation models (FMs) from Amazon and leading AI startups. It uses these models to generate responses based on the retrieved content, supporting generative AI capabilities.
- AWS Lambda: Serverless compute service for executing the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) function. It links content retrieval from Kendra and response generation from Bedrock, functioning in an event-driven manner to process chatbot queries.
- Amazon API Gateway: Interface connecting the chatbot to the backend services. It routes user requests to the Lambda function for processing.
- Amazon CloudFront: Provides content delivery capabilities, ensuring efficient and secure access to the API Gateway, and thus the backend services. It also caches responses to improve performance.